Accelerate IT operations with AI-driven Automation
Automation in IT operations enable agility, resilience, and operational excellence, paving the way for organizations to adapt swiftly to changing environments, deliver superior services, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Driving Innovation with Next-gen Application Management
Next-generation application management fueled by AIOps is revolutionizing how organizations monitor performance, modernize applications, and manage the entire application lifecycle.
AI-powered Analytics: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
AIOps and analytics foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing organizations with actionable intelligence to optimize workflows, enhance service quality, and align IT operations with business goals.
In today’s hyper-competitive digital economy, business leaders are no longer just concerned with the uptime of their applications; they are increasingly obsessed with the performance, resilience, and agility of their entire technology stack. As we dive deeper into the age of intelligent automation, organizations are faced with a critical question: How do we ensure that our systems are not only functioning but also thriving in real-time? The answer lies in the powerful combination of Application Performance Monitoring (APM) and Observability.
Traditional APM, once the cornerstone of IT operations, is now evolving alongside modern observability practices. Together, they are reshaping how organizations detect, diagnose, and resolve issues in complex IT ecosystems. However, the story doesn’t end with better insights. The key to transforming these insights into actionable intelligence lies in intelligent observability, which integrates AI and Machine Learning (AI/ML) to turn data into actionable insights and automate routine responses, enabling IT teams to focus on innovation.
In this blog, we explore how APM and observability are interconnected and how they can collectively power your organization towards a future where performance is optimized, downtime is minimized, and automation is intelligent and self-healing.
Application Performance Monitoring (APM): The Bedrock of Performance Insights
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) is a core discipline focused on providing deep visibility into the health, performance, and availability of software applications. In traditional monitoring, system metrics like CPU usage, memory consumption, and network latency provide useful insights. However, APM takes this further by closely tracking end-to-end transactions across the entire application stack.

Key components of APM typically include:
The Red Ocean Reality:
- Real-time monitoring of application performance across distributed systems.
- Transaction tracing, which tracks individual user requests as they pass through microservices or monolithic systems.
- Error detection and performance bottlenecks, identifying when things go wrong in the stack and why.
- Root cause analysis (RCA), leveraging AI and machine learning to quickly pinpoint the origins of performance degradation or failures.
The iAM Blue Ocean Shift:
As businesses scale into complex, multi-cloud environments, Application Performance Monitoring helps maintain performance by ensuring that issues can be swiftly detected and addressed, often before users even notice disruptions. With APM, real-time visibility into each layer of the technology stack—from frontend to backend—is essential to maintaining consistent, high-quality user experiences.
Observability: A Holistic Approach to System Monitoring
The Value Created:
The concept of observability extends beyond just monitoring and logging—it’s about gathering, correlating, and analyzing all system signals, including metrics, logs, and traces, to gain deep visibility and actionable insights into how an application behaves in production.
When organizations embrace observability, they can understand the why behind performance issues, not just the what. Instead of merely tracking availability and response times, observability allows businesses to gain predictive insights, uncover system anomalies, and ultimately ensure better user experiences.

Experience the future of IT with Qinfinite’s Intelligent Twin. Request for a free demo today!
With iAM, every application becomes a node within a larger, interconnected system. The “intelligent” part isn’t merely about using AI to automate processes but about leveraging data insights to understand, predict, and improve the entire ecosystem’s functionality.
Consider the practical applications:
Observability is defined by three key pillars:
The Red Ocean Reality:
- Metrics provide quantitative data about system performance, such as response times, error rates, and throughput.
- Logs give context to these metrics by recording detailed information about the system’s internal state, such as events, transactions, and errors.
- Traces offer insights into the flow of requests across distributed systems, enabling teams to understand the user journey and identify performance bottlenecks.
Bridging the Gap: How APM Complements Observability
The iAM Blue Ocean Shift:
APM and observability are often seen as two sides of the same coin, each serving a distinct yet complementary role in modern IT ecosystems. While APM focuses on tracking application-specific metrics and user experience, such as response times, transaction traces, and code-level diagnostics. Observability, on the other hand, broadens this perspective by correlating application performance with infrastructure, network, and system-wide data. It connects the dots between system and application layers, providing the context to diagnose and resolve complex, distributed issues effectively.

While APM provide valuable data points, observability integrates and contextualizes this data, addressing challenges like telemetry data overload. With the integration of AI/ML, observability evolves further to enable automated anomaly detection, root cause analysis, and proactive incident prevention. This synergy transforms raw data into actionable intelligence, empowering IT teams to automate responses to recurring issues, optimize performance, and ensure seamless system and application operations.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Challenges in APM and Observability Ecosystems
The Red Ocean Reality:
As enterprise IT landscapes grow in complexity, organizations often deploy various tools for monitoring, APM, observability, and automation, but these tools often operate in silos. While they each serve critical functions, the lack of integration creates significant challenges, such as:
- Fragmented Ecosystem: Enterprises may have solutions for monitoring, APM, observability, and automation, but these tools are rarely linked together to form a seamless flow. This disconnection forces IT teams to manually correlate data across platforms, increasing effort and slowing down problem resolution.
- Data Overload: The sheer volume of telemetry data—logs, traces, metrics, and events—creates “observability fatigue,” making it difficult to separate noise from meaningful signals. Without unified insights, teams struggle to prioritize and act on the data effectively.
- Reactive Problem-Solving: Even with advanced observability platforms, many solutions surface issues only after disruptions have occurred. The lack of predictive capabilities and proactive insights forces teams into firefighting mode rather than preventing incidents.
- Manual Workflows: While automation tools exist, they are often not fully integrated with observability platforms. This leaves teams dependent on manual workflows for issue resolution, slowing down response times, increasing operational costs, and introducing potential errors.
To overcome these challenges, enterprises need a unified approach that integrates monitoring, APM, observability, and automation into a cohesive ecosystem. By leveraging AI/ML-driven intelligence, organizations can connect these tools, eliminate silos, and enable seamless data flow, reducing human intervention and empowering proactive, automated issue resolution.
How AI/ML Bridges the Disconnect in Monitoring and Observability Ecosystems
The integration of AI/ML into observability addresses the fragmentation in enterprise IT ecosystems by creating a seamless flow between monitoring, APM, observability, and automation. Here’s how AI/ML transforms this disconnected landscape into a unified, proactive approach:
1. Unified Anomaly Detection:
AI learns normal behavior patterns across systems and applications, correlating data from multiple sources to flag deviations in real time. This eliminates the need for IT teams to manually piece together anomalies detected by separate tools.
2. Predictive Insights Across Silos:
By analyzing historical trends across monitoring, APM, and observability platforms, AI/ML models forecast potential failures, enabling proactive maintenance. This helps IT teams anticipate issues rather than react after disruptions occur.
3. Integrated Root Cause Analysis:
AI automatically correlates metrics, logs, and traces from disparate tools, surfacing probable root causes within a unified context. This reduces the manual effort required to reconcile data across fragmented systems and speeds up troubleshooting.
4. Automated End-to-End Remediation:
Intelligent platforms powered by AI/ML can execute automated responses, such as restarting services, reallocating resources, or reconfiguring systems. By integrating automation directly into the observability workflow, organizations can resolve issues without human intervention, reducing downtime and operational costs.
AI/ML serves as the glue that connects fragmented monitoring, APM, and observability ecosystems, enabling enterprises to move from reactive firefighting to proactive system optimization. This integration not only enhances efficiency but also allows teams to focus on strategic innovations rather than operational bottlenecks.
Intelligent Observability in Action: The Qinfinite Advantage
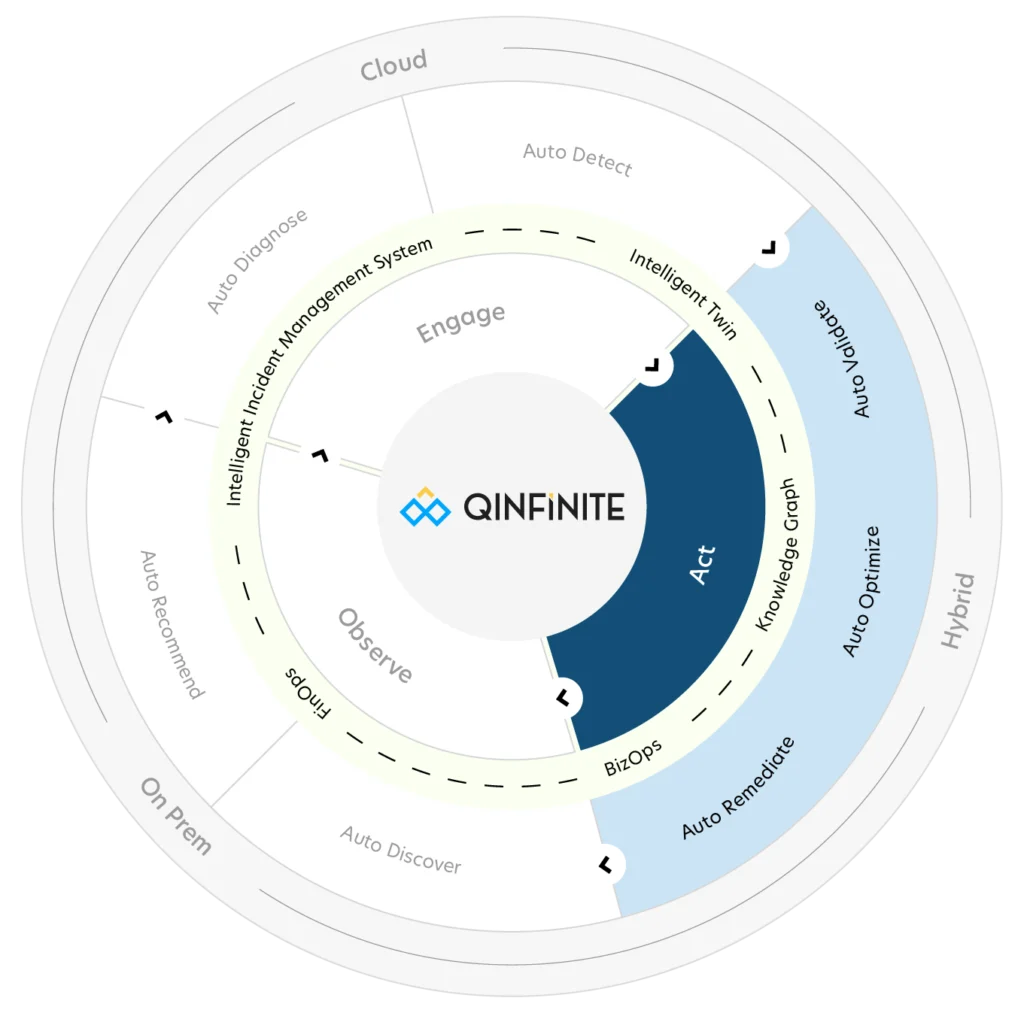
Qinfinite is a next-generation platform that bridges the gap between APM, observability, and automation, creating a unified, AI/ML-driven ecosystem. By interconnecting these critical components, Qinfinite enables businesses to seamlessly transform raw data into actionable intelligence and automate routine incident responses for smooth IT operations.
Key Features of Qinfinite:
1. Auto Discovery and Topology Mapping
- Qinfinite automatically scans and maps the entire IT landscape, building a dynamic, real-time topology of systems and their interdependencies.
- This context is captured in a Knowledge Graph, connecting insights from tools like CloudWatch with observability data for precise impact analysis and better decision-making.
2. Deep Data Analysis
- Qinfinite integrates data from tools like CloudWatch, alongside logs, metrics, traces, and events, leveraging AI/ML to detect patterns, anomalies, and correlations across systems.
- By unifying APM data, observability metrics, and external tool inputs, it provides actionable insights that reveal how incidents impact both IT systems and business outcomes.
3. Intelligent Incident Management
- Qinfinite transforms insights from observability platforms and monitoring tools into automated actions, such as restarting services, scaling infrastructure, or reconfiguring resources.
- This integration reduces Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) by connecting observability insights, external tool data, and automated workflows into a cohesive incident management approach.
4. Seamless Integration with Monitoring Ecosystems
- Qinfinite works alongside tools like AWS CloudWatch, Datadog, and Prometheus to gather telemetry data, providing a single pane of glass for observability and enabling enhanced collaboration across monitoring ecosystems.
Qinfinite leads the evolution toward intelligent observability by seamlessly linking APM, observability, and automation. Its AI-driven capabilities, such as anomaly detection, predictive analysis, and automated remediation, empower enterprises to transform data into intelligent actions, paving the way for the future of IT operations.
5. Breaking Down Silos with Cross-Functional Collaboration and Visibility
The Red Ocean Reality:
In the crowded waters of traditional tools, collaboration across functions is often limited. Each team has its own tools and metrics, leading to siloed insights and fragmented decision-making. Business units, finance, and IT often speak different languages when it comes to application management, making it difficult to achieve true alignment and efficiency.
The iAM Blue Ocean Shift:
iAM creates a unified platform that breaks down silos and fosters cross-functional collaboration. With a single source of truth, everyone—whether in IT, operations, finance, or the C-suite—can access the same real-time insights. It’s like providing the entire crew with a shared compass and map, ensuring everyone knows where they’re headed and why.
The Value Created:
For business leaders, this alignment is invaluable. iAM not only improves communication across departments but also accelerates decision-making. When every stakeholder has visibility into the application ecosystem, teams can work together to solve problems faster, identify opportunities, and align efforts around shared objectives. This collaborative foundation is crucial for executing large-scale transformations successfully.
5. Strategic Cost Optimization and Resource Allocation
How it Works:
iAM goes beyond cost-cutting by enabling strategic cost optimization. By analyzing usage patterns, license costs, and resource consumption, iAM identifies high-impact areas where investment will yield the greatest return. This includes recommending where to increase, decrease, or reallocate resources within the application portfolio, as well as pinpointing areas that could benefit from cloud migration or application modernization.
Business Benefit:

For CxOs, iAM provides a clear path to smarter spending. Instead of blanket budget cuts or speculative investments, leaders get a granular view of where money is being well-spent and where it’s wasted. This allows for a lean, focused technology budget that aligns with business goals and maximizes ROI. In times of economic uncertainty or during rapid growth phases, this strategic resource allocation is invaluable.
6. Accelerated Product Development and Time-to-Market
How it Works:
By streamlining the development and deployment process, iAM can help organizations launch products and features faster. Automated testing, dependency mapping, and real-time monitoring ensure that applications are deployed smoothly and perform reliably. iAM’s continuous discovery process also surfaces reusable assets, code libraries, or APIs within the organization, which can speed up development cycles for new products.
Business Benefit:
In competitive markets, speed matters. For CxOs, iAM’s impact on time-to-market can be a game-changer. With accelerated product development cycles, businesses can capitalize on new opportunities quickly and stay ahead of competitors. This translates into a direct revenue impact and enhances the organization’s reputation as an innovative, responsive player in its industry.
7. Enhanced Collaboration and Cross-Functional Visibility
How it Works:
With iAM, everyone from IT to business units has a shared, real-time view of the application ecosystem. This transparency fosters better collaboration and alignment, as each department can see how applications contribute to overall business goals. Automated workflows and notifications keep stakeholders informed, reducing the back-and-forth and siloed decision-making that often bogs down large organizations.
Business Benefit:
For executives, streamlined collaboration and cross-functional visibility lead to faster, more informed decision-making. iAM minimizes organizational silos, aligning departments towards common objectives. This increased collaboration speeds up problem resolution, boosts productivity, and drives accountability across teams. When everyone can see the full picture, alignment becomes effortless, empowering the entire organization to move in unison towards strategic goals.
In the Infinite Game of application management, you can’t rely on tools designed for finite goals. You need a platform that understands the ongoing nature of application management and compounds value over time. Qinfinite is that platform that has helped businesses achieve some great success numbers as listed below:
The Intelligence Layer: iAM as the Digital Conductor
Think of iAM as a digital conductor in an orchestra, where every application is an instrument. While each instrument has its distinct role and sound, it’s the conductor that ensures harmony, aligning each player’s timing and tone. iAM platforms gather data from every application, continuously analyzing and optimizing to ensure the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.
For CxOs, this is revolutionary. Rather than spending time and money wrangling disparate applications and tools, iAM provides a unified layer of intelligence, offering a single pane of glass for managing, monitoring, and optimizing your entire application portfolio.
Here’s where iAM brings an executive value-add:
- Strategic Decision-Making: Imagine being able to visualize which applications drive the most impact on your revenue and growth or identify gaps where investment might be needed. iAM aggregates and visualizes application performance data, translating it into insights that fuel smarter business decisions.
- Reduced Operational Complexity: iAM reduces the need to rely on ad-hoc integrations or constantly switch between applications. With this intelligent layer, it’s like having a translator that helps all applications “speak” to each other, streamlining operations across departments.
- Enhanced Agility: In the fast-paced digital economy, you need to pivot and scale quickly. iAM enables businesses to scale applications up or down, onboard new ones, and offboard redundant systems seamlessly—all while minimizing risk.
Real-World Success: iAM in Action
Let’s consider a real-world example to bring iAM’s value to life.
Take a retail company with a complex ecosystem of applications—POS systems, inventory management, e-commerce platforms, customer service chatbots, and more. Traditionally, if the e-commerce site experiences an outage, customer service suffers, inventory updates get delayed, and sales are lost. Fixing these issues often requires a patchwork of support from multiple teams, increasing downtime and frustration.
With iAM in place, the system recognizes the interdependencies in real time. If a slowdown is detected on the e-commerce platform, iAM alerts relevant stakeholders, prioritizes troubleshooting based on the potential business impact, and even re-routes customer service channels to manage inquiries more effectively until the issue is resolved.
The iAM layer’s intelligence doesn’t just provide a temporary fix—it continuously learns and adapts, making future incidents less disruptive and giving the C-suite confidence that operations are resilient and responsive.
The Road Ahead: How iAM Will Shape the Future of Digital Enterprises
We’re just scratching the surface of iAM’s potential. As technology evolves, iAM will integrate more advanced AI models, predictive analytics, and machine learning to drive even more precise insights. Think of iAM as a platform that will increasingly bridge the gap between business goals and technical execution, empowering organizations to evolve with speed and precision.
Imagine a world where iAM automatically aligns your application ecosystem to seasonal demand fluctuations, prioritizes resources based on changing customer behaviors, and identifies new growth opportunities based on patterns it detects in usage data. For a CxO, this isn’t just application management—it’s intelligent business orchestration.
1. Auto Discovery and Topology Mapping:
Qinfinite’s Auto Discovery continuously scans and maps your entire enterprise IT landscape, building a real-time topology of systems, applications, and their dependencies across business and IT domains. This rich understanding of the environment is captured in a Knowledge Graph, which serves as the foundation for making sense of observability data by providing vital context about upstream and downstream impacts.
2. Deep Data Analysis for Actionable Insights:
Qinfinite’s Deep Data Analysis goes beyond simply aggregating observability data. Using sophisticated AI/ML algorithms, it analyzes metrics, logs, traces, and events to detect patterns, anomalies, and correlations. By correlating this telemetry data with the Knowledge Graph, Qinfinite provides actionable insights into how incidents affect not only individual systems but also business outcomes. For example, it can pinpoint how an issue in one microservice may ripple through to other systems or impact critical business services.
3. Intelligent Incident Management: Turning Insights into Actions:
Qinfinite’s Intelligent Incident Management takes observability a step further by converting these actionable insights into automated actions. Once Deep Data Analysis surfaces insights and potential root causes, the platform offers AI-driven recommendations for remediation. But it doesn’t stop there, Qinfinite can automate the entire remediation process. From restarting services to adjusting resource allocations or reconfiguring infrastructure, the platform acts on insights autonomously, reducing the need for manual intervention and significantly speeding up recovery times.
By automating routine incident responses, Qinfinite not only shortens Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) but also frees up IT teams to focus on strategic tasks, moving from reactive firefighting to proactive system optimization.
Did you know? According to a report by Forrester, companies using cloud-based testing environments have reduced their testing costs by up to 45% while improving test coverage by 30%.
Final Thoughts: iAM as the Blue Ocean of Intelligent Application Management
In a market saturated with incremental improvements, iAM stands out by creating a blue ocean—a space of its own, free from the red ocean of fragmented, reactive, and isolated tools. Intelligent Application Management isn’t about competing on the same metrics as traditional solutions; it’s about redefining what application management can be. iAM brings holistic visibility, continuous optimization, predictive insights, and strategic alignment to the table—ushering in a new era of application management that empowers organizations to thrive, not just survive.
For CxOs, iAM is more than a solution; it’s a new way to navigate the digital seas. It’s the compass and the map, charting a course through uncharted waters and creating a sustainable competitive advantage. In the blue ocean of iAM, the competition becomes irrelevant, and organizations are empowered to realize their fullest potential, transforming application management from a cost center into a strategic enabler of growth and innovation.
Tired of reactive IT and siloed data? Qinfinite goes beyond traditional application management with its next-generation features like Intelligent Twin, Enterprise Knowledge Graph, AIOps, Intelligent Incident Management and BizOps integration for unmatched visibility, problem-solving and business aligned optimization. Request for a free demo today!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
IT monitoring involves collecting predefined metrics from applications, infrastructure, and networks to provide a snapshot of their current state. It answers what is happening by tracking system-level metrics like CPU usage, memory consumption, or network traffic. However, it lacks the depth to explain why issues occur, focusing on basic system health rather than application-specific insights. IT Monitoring is primarily reactive, alerting teams when predefined thresholds are breached, leaving IT teams to manually investigate the root cause. predictive insights, and continuous optimization, empowering business leaders to align technology with strategic goals and drive transformation.
APM builds upon traditional monitoring by specifically tracking how applications perform from both a technical and user experience perspective. It dives deeper into metrics like transaction times, error rates, and database queries, helping IT teams identify why performance issues occur in the application layer. APM provides visibility into code-level bottlenecks, slow APIs, and user transactions, enabling faster root cause analysis and optimizing application performance. While monitoring focuses on systems, APM narrows its scope to applications, bridging the gap between infrastructure and end-user experience.
Observability extends beyond monitoring and APM, providing a holistic view of why systems and applications behave the way they do. It combines metrics, logs, traces, and contextual events to infer the internal state of systems. Observability is crucial in modern distributed, cloud-native architectures where pinpointing issues across microservices, APIs, and networks requires a system-wide perspective. By correlating data from both infrastructure and application layers, observability enables proactive identification of potential failures and provides insights into upstream and downstream impacts.
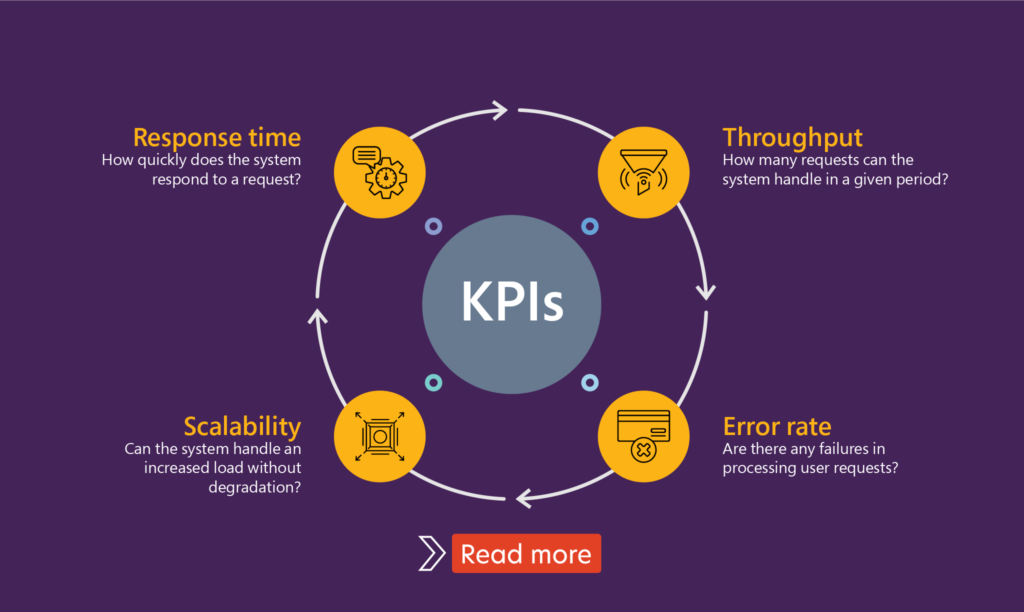
APM focuses on specific performance metrics, such as application response times, latency, throughput, and error rates. It provides real-time insights to identify issues.
Observability, on the other hand, is about gaining a deeper understanding of system behavior by collecting and correlating three pillars of data: metrics, logs, and traces. Observability helps uncover why issues occur and offers insights into how to fix them.
Yes, APM and observability can be used independently, but they are most effective when combined:
-APM without Observability can help track application performance, but it lacks the depth and context required to fully understand system behavior or to quickly pinpoint the cause of issues.
– Observability without APM can provide detailed traces and logs, but without the performance-focused metrics from APM, teams might struggle to identify and address real-time performance issues.
Together, they offer a comprehensive view of system health, from high-level performance indicators to low-level root cause analysis.
By combining APM and observability data, organizations can build intelligent automation systems that are proactive rather than reactive. Automation tools can use insights from APM (like response time spikes or increased error rates) and data from observability platforms (like detailed logs and traces) to:
-Automatically trigger alerts and remediation processes when an issue arises.
-Self-heal by adjusting system resources or scaling based on observed performance metrics.
-Predict performance issues before they become critical, allowing teams to address potential failures before they impact users.
-Faster troubleshooting: APM helps identify performance issues, while observability provides the context to diagnose and fix them quickly.
-Better root cause analysis: By correlating APM metrics with logs and traces, teams can understand the underlying causes of problems rather than just symptoms.
-Optimized performance: Combining APM’s performance tracking with observability’s deep visibility allows businesses to continuously monitor and optimize system performance across all components.
-Improved customer experience: With proactive monitoring and automation, businesses can prevent performance issues from impacting users, improving reliability and satisfaction.
In a DevOps environment, APM and observability are crucial for ensuring continuous delivery and deployment pipelines. With APM, teams can monitor the performance of applications in real-time during development and production stages. Observability enables them to quickly diagnose issues, understand system behavior, and implement rapid fixes. This synergy leads to faster releases, more reliable applications, and ultimately supports agile, high-performing DevOps teams.
In large, distributed environments, APM and observability are indispensable. APM tracks performance metrics across various services, while observability provides traceability and logs to monitor microservices, containers, and cloud environments. By using both, teams can ensure that performance remains consistent across a growing infrastructure, identify scaling bottlenecks, and optimize resource allocation in real-time. This makes scaling applications more manageable, reducing the risk of performance degradation as infrastructure expands.
Both APM and observability provide valuable insights into application behavior over time. By continuously monitoring performance metrics and collecting detailed logs and traces, organizations can:
-Identify performance trends and areas for improvement.
-Perform iterative optimizations based on real-time data.
–Track the impact of changes to ensure that optimizations lead to sustained performance improvements.
Organizations should prioritize:
-End-to-end visibility: Implement tools that provide visibility across the entire application stack, from the frontend to the backend.
-Data correlation: Ensure that APM and observability tools are integrated to correlate metrics, logs, and traces for deeper insights.
-Automation: Leverage intelligent automation to act on the insights provided by APM and observability platforms, improving response times and system resilience.
-Proactive monitoring: Continuously monitor performance and look for opportunities to optimize systems before issues arise.
